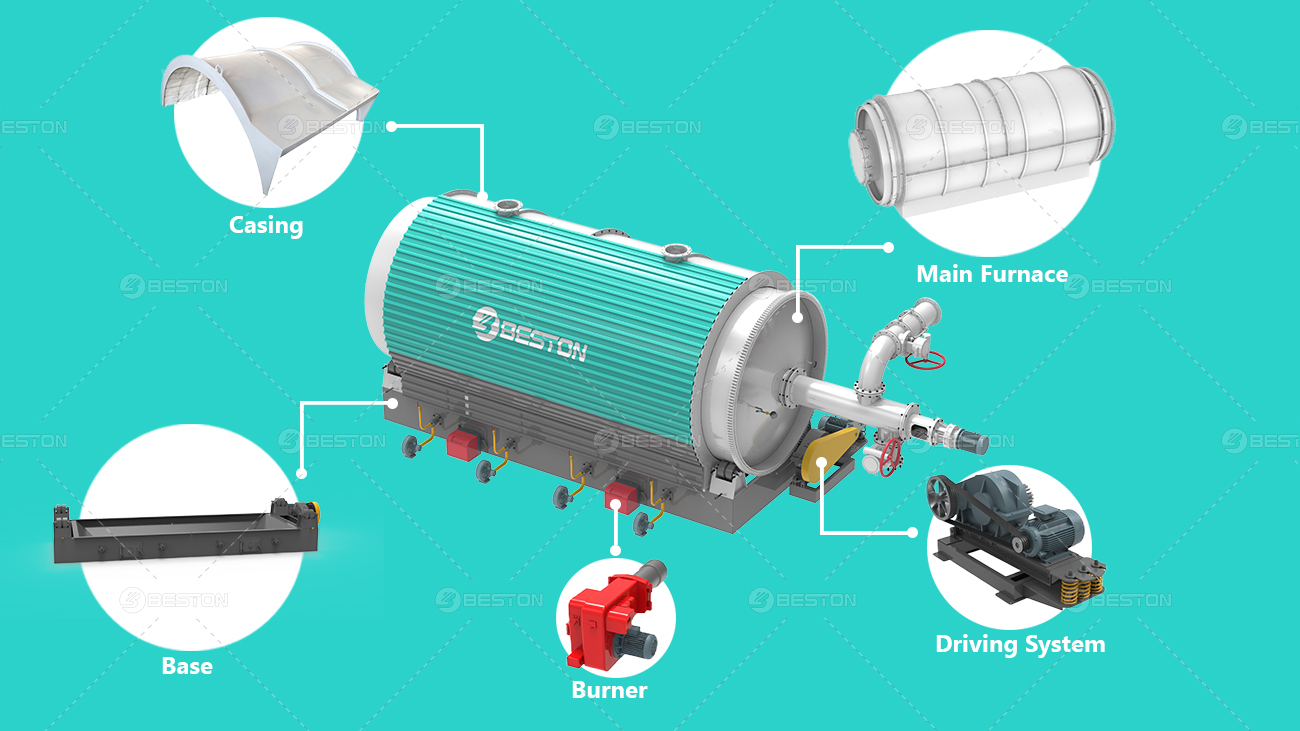
Managing oil sludge, a by-product of petroleum extraction and refining, has become increasingly critical due to its environmental and operational implications. Among available treatment technologies, pyrolysis has emerged as a leading solution for converting oil sludge into reusable resources. The efficiency of this process, however, is significantly influenced by the moisture content of the feedstock. In an oil sludge pyrolysis plant, understanding and managing this variable is pivotal to achieving optimal performance.
Characteristics of Oil Sludge and Pyrolysis Process
Oil sludge is a complex mixture of water, hydrocarbons, and solids, often containing hazardous substances. Pyrolysis, a thermal degradation process performed in the absence of oxygen, transforms oil sludge into valuable products such as pyrolysis oil, gas, and char. The efficiency and yield of these products depend on several factors, with moisture content being a critical determinant.
High moisture levels in oil sludge can impede the pyrolysis reaction by consuming additional energy to evaporate the water. Conversely, excessively dry feedstock may increase risks related to reactor stability and overheating. Striking a balance in moisture content is thus essential to maximize resource recovery and minimize operational inefficiencies.

Impact of Moisture Content on Pyrolysis Efficiency
1. Energy Consumption
In an oil sludge pyrolysis equipment, moisture content directly impacts energy requirements. Sludge with high water content demands significant energy input to vaporize the water before the pyrolysis reaction can proceed. This additional energy consumption lowers the thermal efficiency of the process, reducing the net energy available for pyrolyzing hydrocarbons.
For instance, sludge with a 50% moisture content could require nearly twice the energy compared to feedstock with 10% moisture. This increased energy demand not only affects operating costs but also diminishes the overall economic viability of the plant.
2. Product Yield
Moisture content also influences the yield and quality of pyrolysis products. Excessive moisture can dilute the pyrolysis oil, reducing its calorific value and commercial desirability. Additionally, high water content may result in incomplete pyrolysis of hydrocarbons, leading to lower oil and gas yields and an increased proportion of unprocessed char.
On the other hand, sludge that is too dry can accelerate the thermal decomposition of hydrocarbons, potentially leading to over-cracking and the production of excess syngas at the expense of liquid oil. Maintaining a moderate moisture level is key to ensuring a balanced and efficient product distribution.
3. Reactor Performance and Longevity
The presence of water in oil sludge can have both beneficial and adverse effects on reactor performance. Moderate moisture levels can help regulate reactor temperature and prevent overheating, which is particularly critical for maintaining operational stability in high-capacity oil sludge pyrolysis plants. However, excessive moisture may lead to uneven heating, increased wear on reactor components, and prolonged processing times.
Reactor corrosion is another concern associated with high moisture content. Water, combined with impurities in oil sludge, can form acidic compounds under pyrolysis conditions, accelerating the degradation of reactor materials. Proper moisture control thus extends equipment lifespan and reduces maintenance costs.
Strategies to Optimize Moisture Content
1. Pre-Drying Techniques
Pre-drying oil sludge is one of the most effective methods for managing moisture content. Techniques such as solar drying, mechanical dewatering, or the use of waste heat from the pyrolysis process can significantly reduce moisture levels. By incorporating these methods, operators can minimize energy loss and improve process efficiency.
2. Feedstock Blending
Blending oil sludge with materials of lower moisture content, such as dry biomass or industrial waste, can help achieve an optimal feedstock composition. This approach not only balances moisture levels but also allows the co-processing of different waste streams, increasing the versatility of the pyrolysis plant.
3. Real-Time Monitoring and Control
Advanced oil sludge pyrolysis plants are equipped with sensors and control systems that monitor moisture content in real time. These systems adjust process parameters, such as reactor temperature and heating rate, to accommodate variations in feedstock moisture, ensuring consistent performance.
Economic and Environmental Considerations
The management of moisture content in oil sludge not only impacts operational efficiency but also determines the economic and environmental outcomes of the pyrolysis process. Reducing energy consumption and maximizing resource recovery directly enhance the profitability of the plant. Furthermore, by converting oil sludge into valuable products and minimizing energy waste, pyrolysis contributes to sustainable waste management practices and reduces the carbon footprint of industrial operations.
Conclusion
Moisture content is a decisive factor in the efficiency of oil sludge pyrolysis. Balancing this variable requires a combination of pre-treatment strategies, real-time process control, and optimal reactor design. By addressing the challenges posed by water in oil sludge, operators can improve product yields, reduce costs, and ensure the sustainable operation of oil sludge pyrolysis plants. As the demand for environmentally responsible waste management continues to grow, refining such processes will play a pivotal role in the industry's future.